Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 9(3), p.JFST0055_1 - JFST0055_13, 2014/09
Wall pressure measurements were conducted for a 90 degree elbow of which the axis curvature coincided with its inner diameter (125 mm). Results showed that distributions of fluctuating normalized pressures obtained here and those made by Shiraishi et al. (2006) for the Reynolds number of 3,250,000 coincided within 0.02 of the dynamic pressure. The peak intensity having the Strouhal number of 0.5 was quantitatively in accordance with that of the data obtained in the experimental setup that Shiraishi et al. used (Yamano et al., 2011), suggesting that the law of dynamical similarity could be applied with regard to this oscillation. Cross correlations of pressure fluctuations showed that the pressure fluctuation having the Strouhal number of 0.5 propagated as a planar wave with the bulk velocity.
Naoe, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kenny, R.*; Otsuki, Masato*
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 9(1), p.JFST0002_1 - JFST0002_12, 2014/01
A broad investigation into the hydrodynamics of liquid mercury has been motivated of late by its use in spallation neutron sources. One area of particular concern relates to the erosion suffered by vessel walls from the cumulative effects of liquid mercury droplet impacts arising from the collapse of cavitation bubbles. The low speed (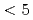 m/s) range of such events forms the focus of this paper and to this end a series of experiments is conducted on spherical droplets of diameter 2.5 mm impacting upon a dry quartz surface. A reasonable simulation of such impacts is made possible by using the VOF solver in combination with an empirical expression for the dynamic contact angle. This latter represents a `best fit' to data obtained from high resolution imaging of the droplet profile for a range of contact line velocities. Experiment and simulation are subsequently compared throughout the stages of initial deposition, spread, recession with break-up and, finally, bounce.
m/s) range of such events forms the focus of this paper and to this end a series of experiments is conducted on spherical droplets of diameter 2.5 mm impacting upon a dry quartz surface. A reasonable simulation of such impacts is made possible by using the VOF solver in combination with an empirical expression for the dynamic contact angle. This latter represents a `best fit' to data obtained from high resolution imaging of the droplet profile for a range of contact line velocities. Experiment and simulation are subsequently compared throughout the stages of initial deposition, spread, recession with break-up and, finally, bounce.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Sago, Hiromi*; Hirota, Kazuo*; Hayakawa, Satoshi*; Xu, Y.*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Sakai, Takaaki
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 7(3), p.329 - 344, 2012/09
As part of the development of a flow-induced vibration evaluation methodology for the primary cooling piping in Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor, important factors were discussed in evaluating the flow-induced vibration for the hot-leg piping. To investigate a complex flow near the inlet of the hot-leg piping, a reactor scale numerical analysis was carried out for the reactor upper plenum flow, which was simulated in a 1/10-scale reactor upper plenum experiment. Based on this analysis, experimental conditions on swirl inflow and deflected inflow that were identified as important factors were determined for flow-induced vibration experiments simulating only the hot-leg piping. In this study, the effect of the swirl inflow on flow pattern and pressure fluctuation onto the pipe wall was investigated in a 1/3-scale hot-leg pipe experiment. The experiment has indicated less significant for the pressure fluctuations, while the flow separation region was slightly influenced by the swirl flow. Computational fluid dynamics simulation results also appear in this paper, focusing on its applicability to the hot-leg piping experiments.
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Kondo, Manabu*; Minamiura, Hirotaka*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 7(3), p.315 - 328, 2012/08
LDV measurements in a 90 degree elbow of which the curvature radius coincides with its inner diameter were examined for the cases of inflow from a long pipe, short pipe and swirl generator. Ensemble averaged flow distribution at the Reynolds number of 320000 based on the inner pipe diameter and bulk velocity shows that shortening the upstream pipe length to 4.9D from 10D induces the flow separation downstream of the elbow.
Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 4(3), p.711 - 722, 2009/10
A high-precision simulation algorithm for gas-liquid two-phase flows on unstructured meshes has been developed to simulate gas entrainment phenomenon in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. In this study, it became clear that unphysical behaviors near gas-liquid interfaces were caused by conventional algorithms. Then, physics-basis considerations were conducted for mechanical balances at gas-liquid interfaces to derive appropriate formulations for velocity and pressure. As the validation test, the rising gas bubble in liquid was simulated by the developed simulation algorithm with the physically appropriate formulations, and the simulated terminal bubble shapes on the structured and highly-distorted unstructured meshes coincided with the experimental data under each simulation condition.
Shiraishi, Tadashi*; Watakabe, Hisato*; Sago, Hiromi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 4(2), p.430 - 441, 2009/00
For the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor, an experimental study on the fluctuating pressure of the hot legs was carried out with tests using a 1/3-scale model. The total resistance coefficient is consistent with the published data, and our research has given some additional data up to the Reynolds number of 8.0 10
10 . The flow pattern in the postcritical regime is independent of a Reynolds number. The statistical examination revealed that fluctuating pressures on the pipe wall depend on the mean velocity but not on the viscosity of the fluid. Negative spikes of pressure appeared for high velocity. Based on these experimental data it is concluded that, there are similarity laws for the scale of a model and the property of fluid, but not for the velocity in the pipe. Theoretical considerations also gave a discussion how to extrapolate the fluctuating pressure to the actual hot-leg conditions.
. The flow pattern in the postcritical regime is independent of a Reynolds number. The statistical examination revealed that fluctuating pressures on the pipe wall depend on the mean velocity but not on the viscosity of the fluid. Negative spikes of pressure appeared for high velocity. Based on these experimental data it is concluded that, there are similarity laws for the scale of a model and the property of fluid, but not for the velocity in the pipe. Theoretical considerations also gave a discussion how to extrapolate the fluctuating pressure to the actual hot-leg conditions.
Ito, Takayuki*; Furuya, Shiho*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 3(4), p.553 - 562, 2008/06
This paper introduces our own hierarchical data visualization technique, Heiankyo View, and discusses its potential for fluid science. Heiankyo View represents hierarchy as nested rectangles, and displays thousands of data elements in one display space. The paper briefly introduces the algorithm and various applications of Heiankyo View, and discusses our attempts for visualization of atomic plant data using Heiankyo View.
Nakayama, Hiromasa; Tamura, Tetsuro*; Abe, Satoshi*
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 3(4), p.519 - 532, 2008/00
Large-eddy simulation is applied to the problem of plume dispersion in convective boundary layer (CBL) flow, which is time-sequentially generated by unsteady numerical simulation of spatially-developing boundary layer capped by a temperature inversion in the driver unit. Our objective is to investigate the characteristics of plume dispersion in CBL flow compared with the case in the neutral boundary layer.
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Takase, Kazuyuki
Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (Internet), 3(2), p.311 - 322, 2008/00